Scientists discover new behavior of membranes that could lead to unprecedented separations
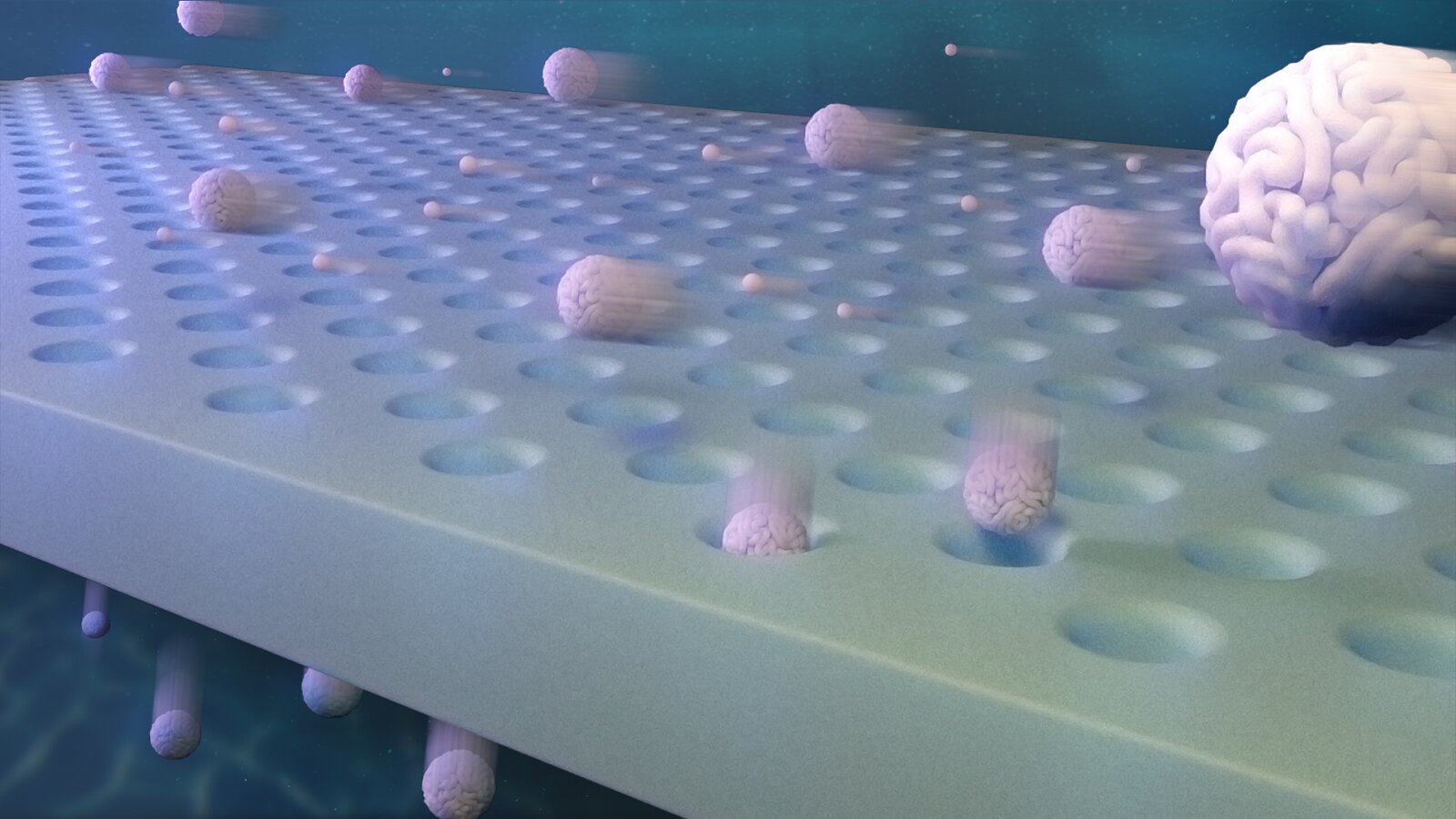
Nanoscale solutes with only small differences in size can be separated by membranes with identical pores – if they have enough opportunities to try. Credit: Argonne National Laboratory. Imagine a basketball game that comes down to the last shot. The chance of the ball going through the hoop may be quite small, but it would … Read more