Phage viruses, used to treat antibiotic resistance, gain an advantage by blocking the reproductive capacity of competitors
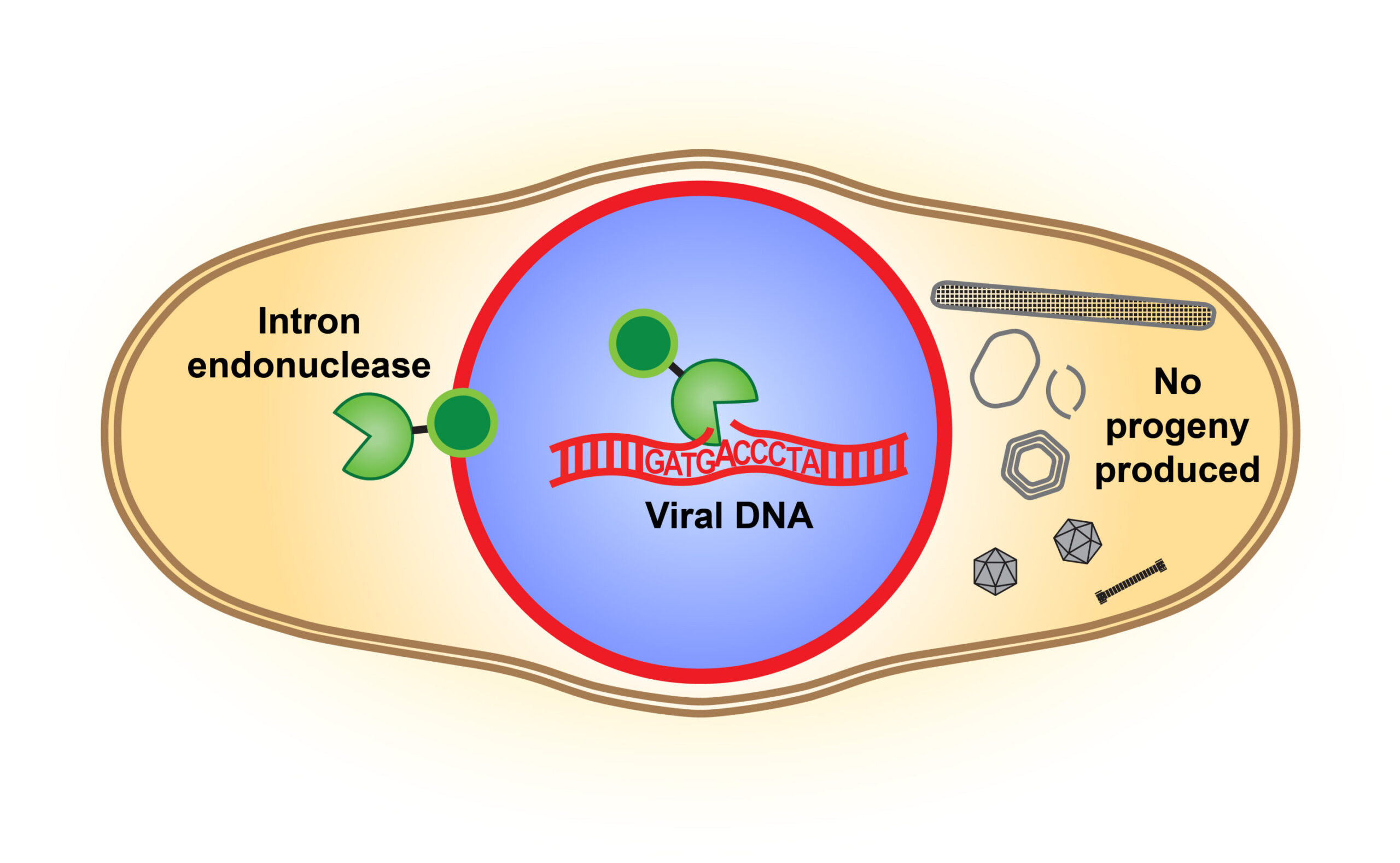
An illustration of the intron endonuclease cutting the DNA of a competing virus and disrupting its reproduction. Credit: Pogliano Labs, UC San Diego Strange bits of DNA hidden in the genomes of all living things have historically been ignored because they seemed to play no role in the fight for survival, researchers thought. These bits … Read more