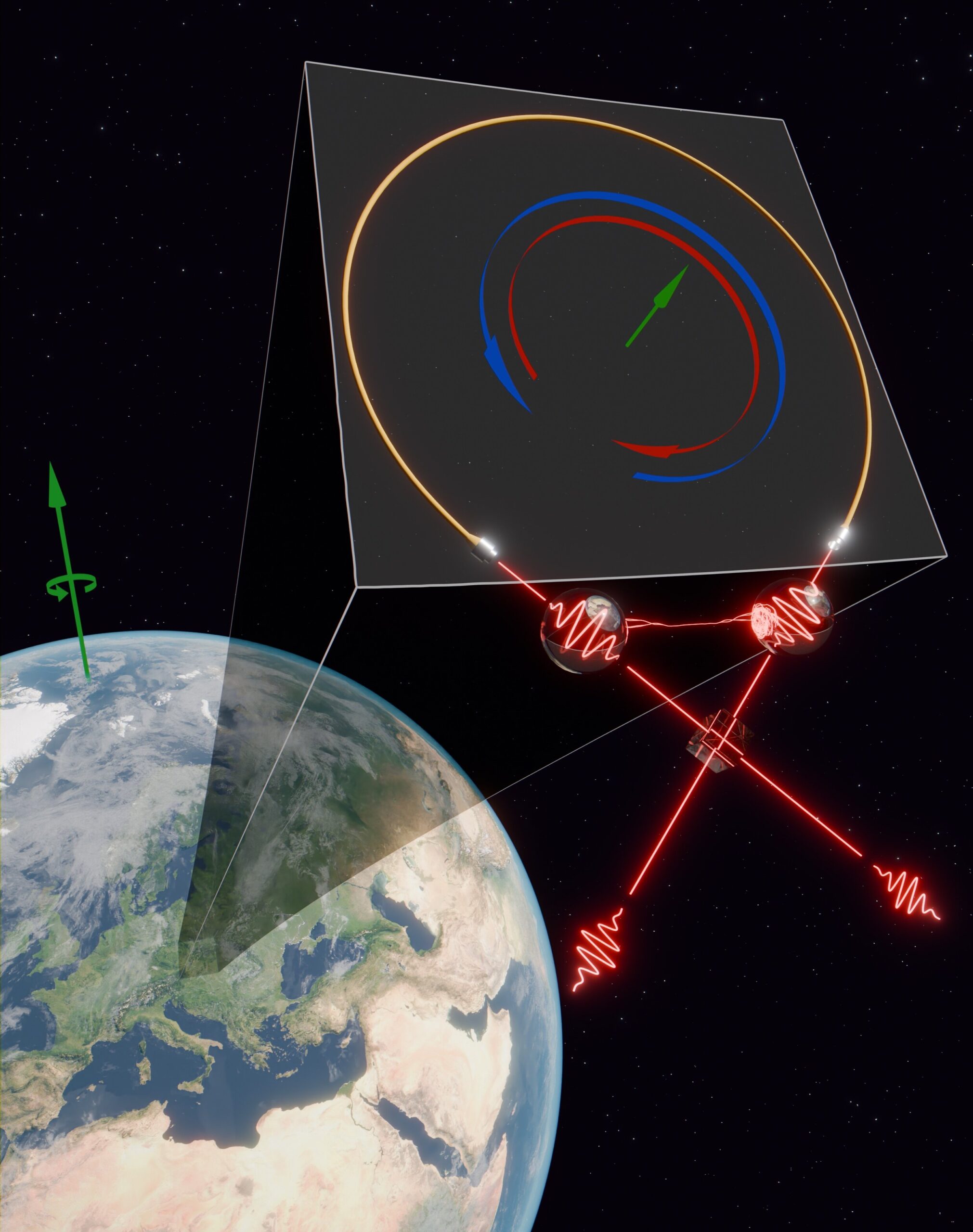
Quantum entangled photons respond to the Earth’s rotation
The experiment was depicted by drawing a Sagnac interferometric fiber scheme in a magnifying inset, starting from a local position (Vienna, Austria) of the rotating Earth. Two indistinguishable photons impinge on a beam splitter cube, entanglement occurs between them and then they are coupled in the fiber interferometer. Credit: Marco Di Vita A team of … Read more