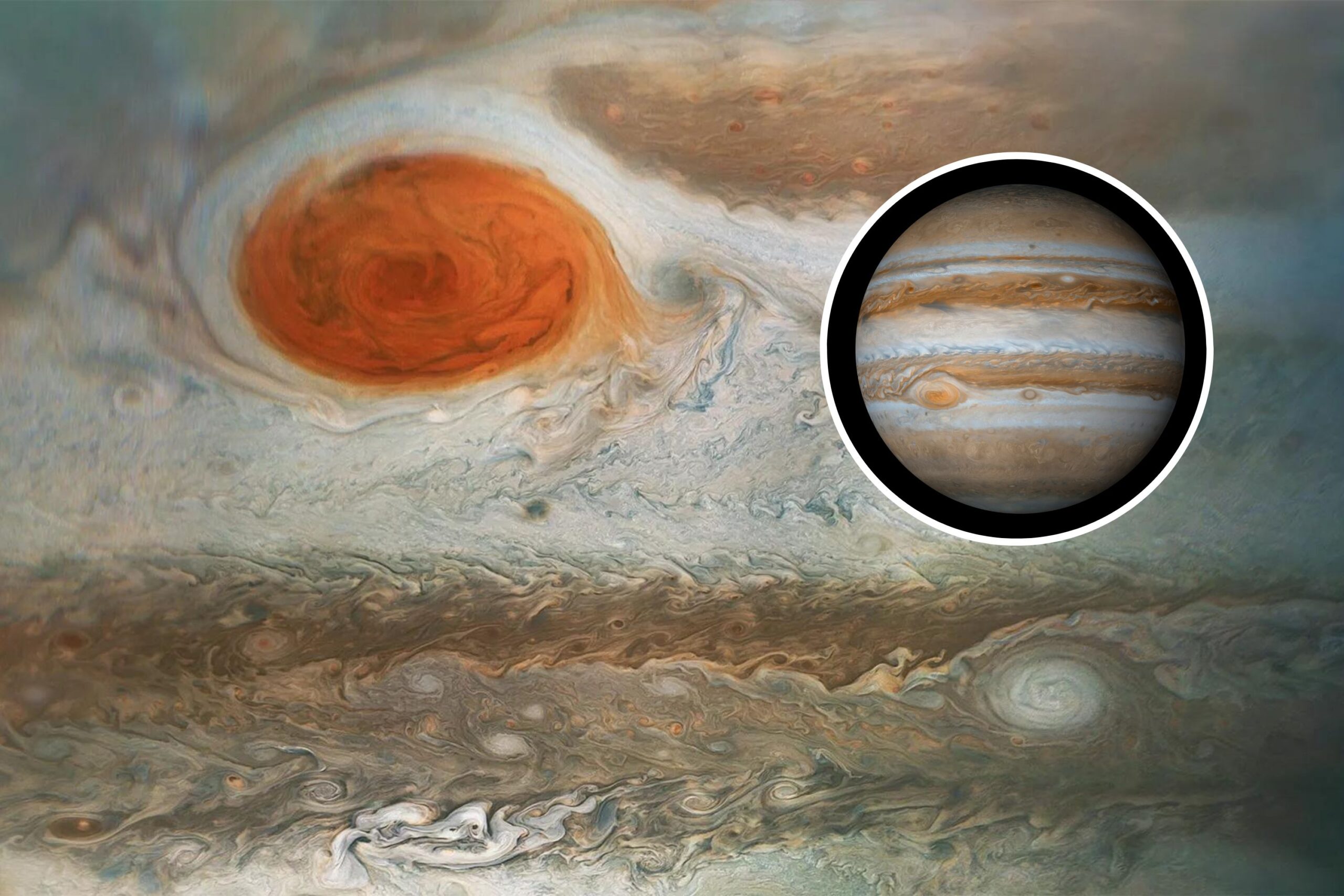
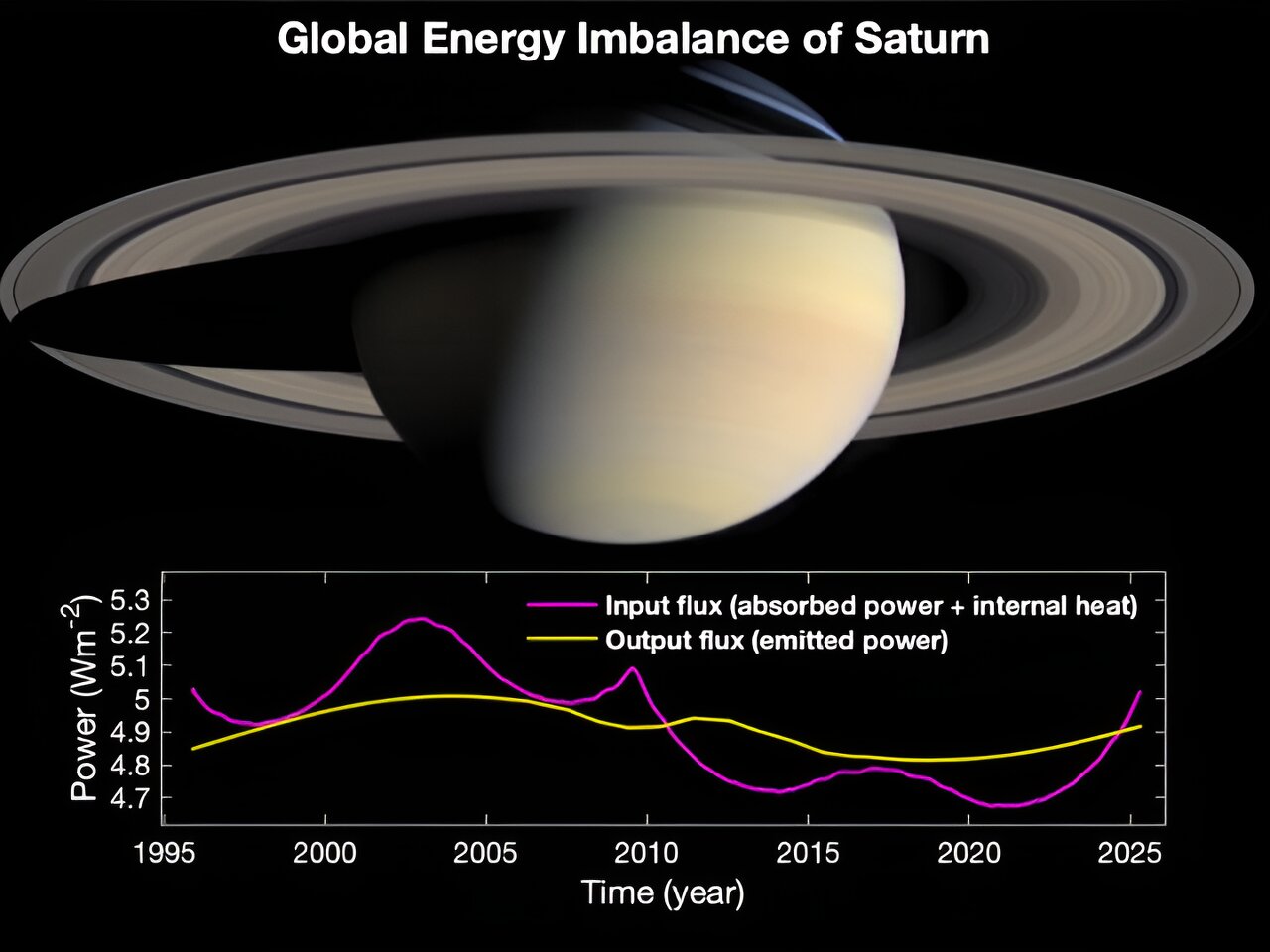
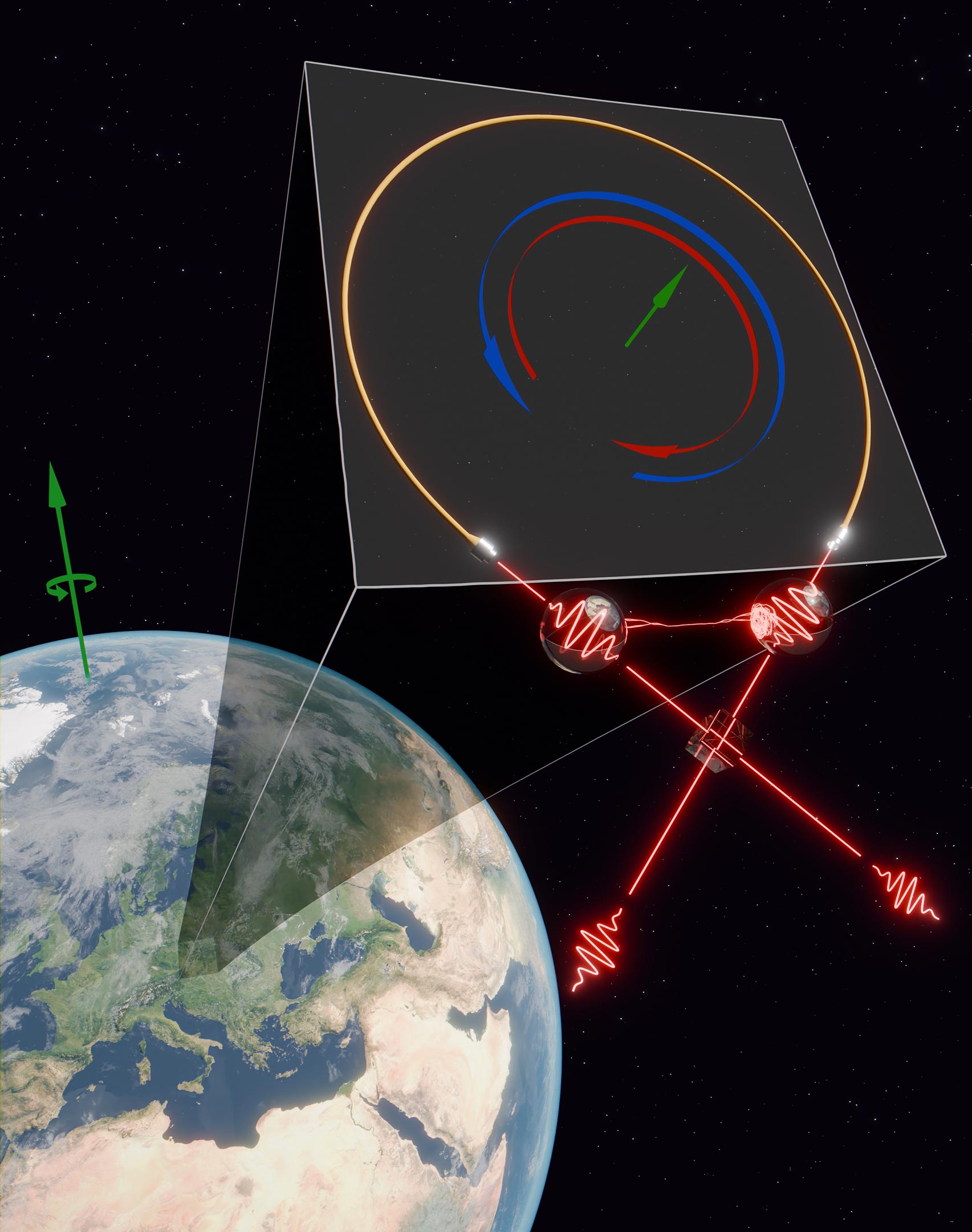
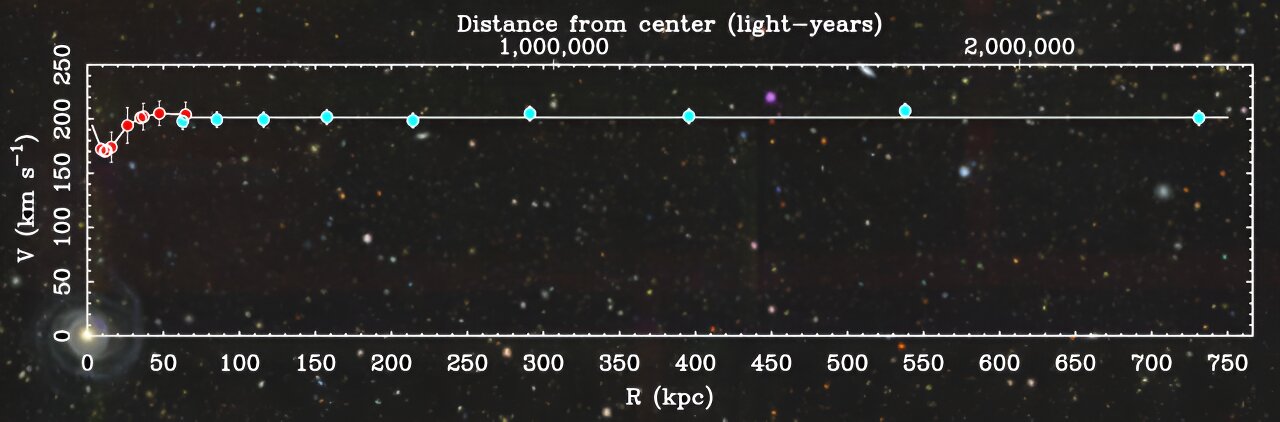
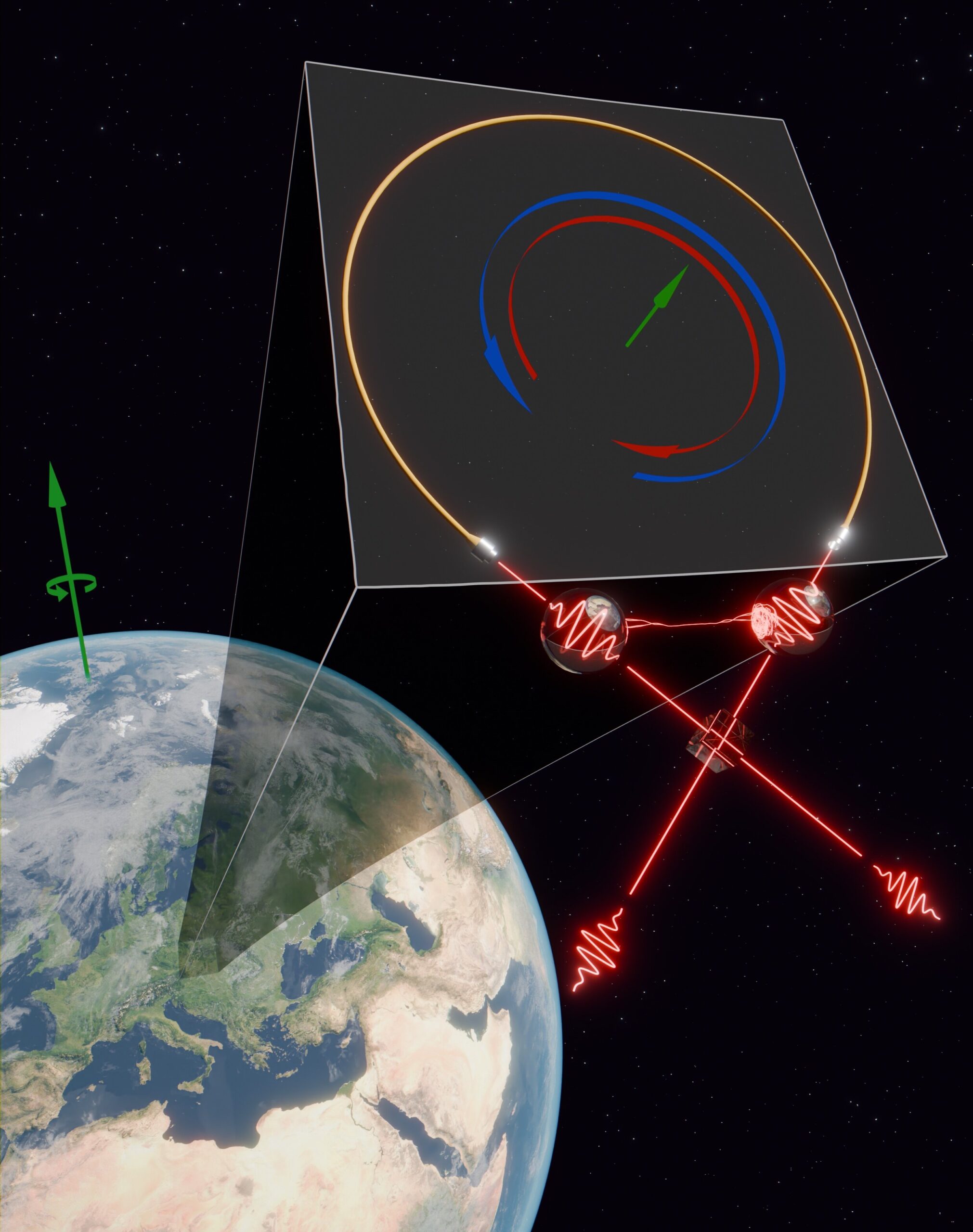
Secrets of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot Revealed
Jupiter has long been famous for its Great Red Spot, but only recently did scientists learn more about how and how long ago it formed. The enormous vortex on the side of the solar system’s largest planet is a massive storm, long thought to have raged for more than 300 years, and larger than the … Read more