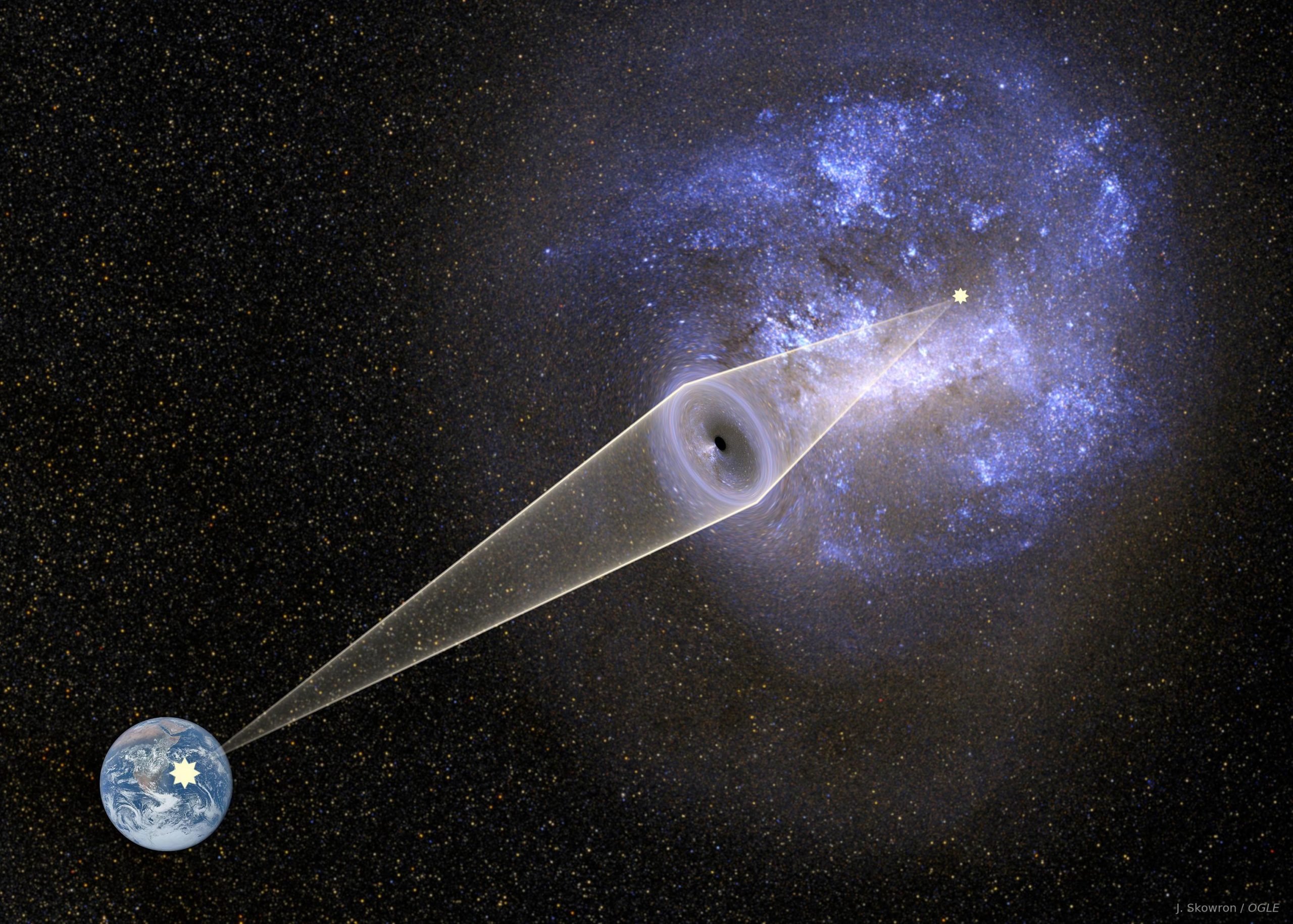
Rapidly cooling weird creatures rewrite the physics of neutron stars
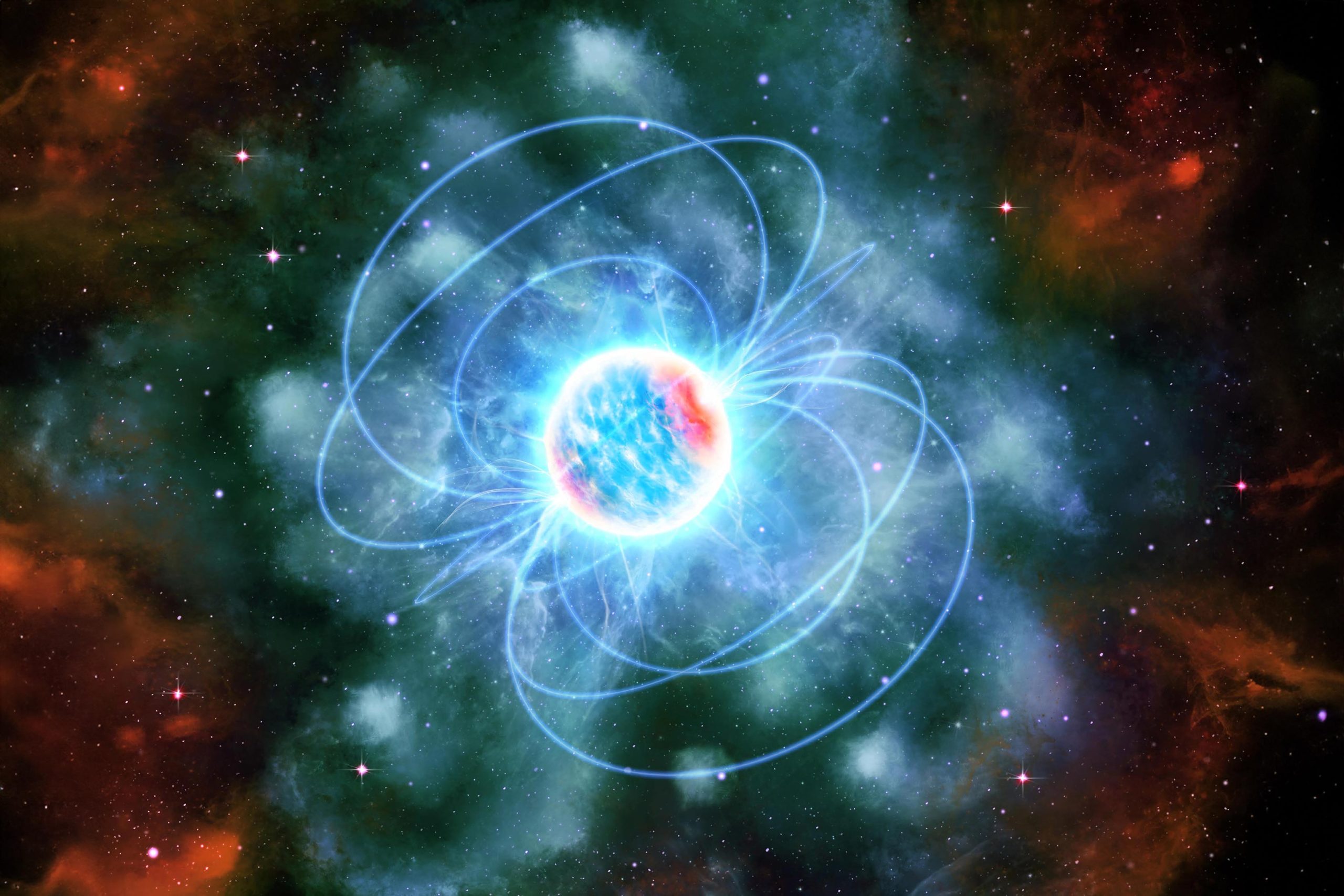
Neutron stars are among the densest objects in the universe. The material inside them is so tightly compressed that scientists don’t yet know what shape it takes. The core of a neutron star may be a thick soup of quarks, or it may contain exotic particles that could not survive anywhere else in the universe. … Read more