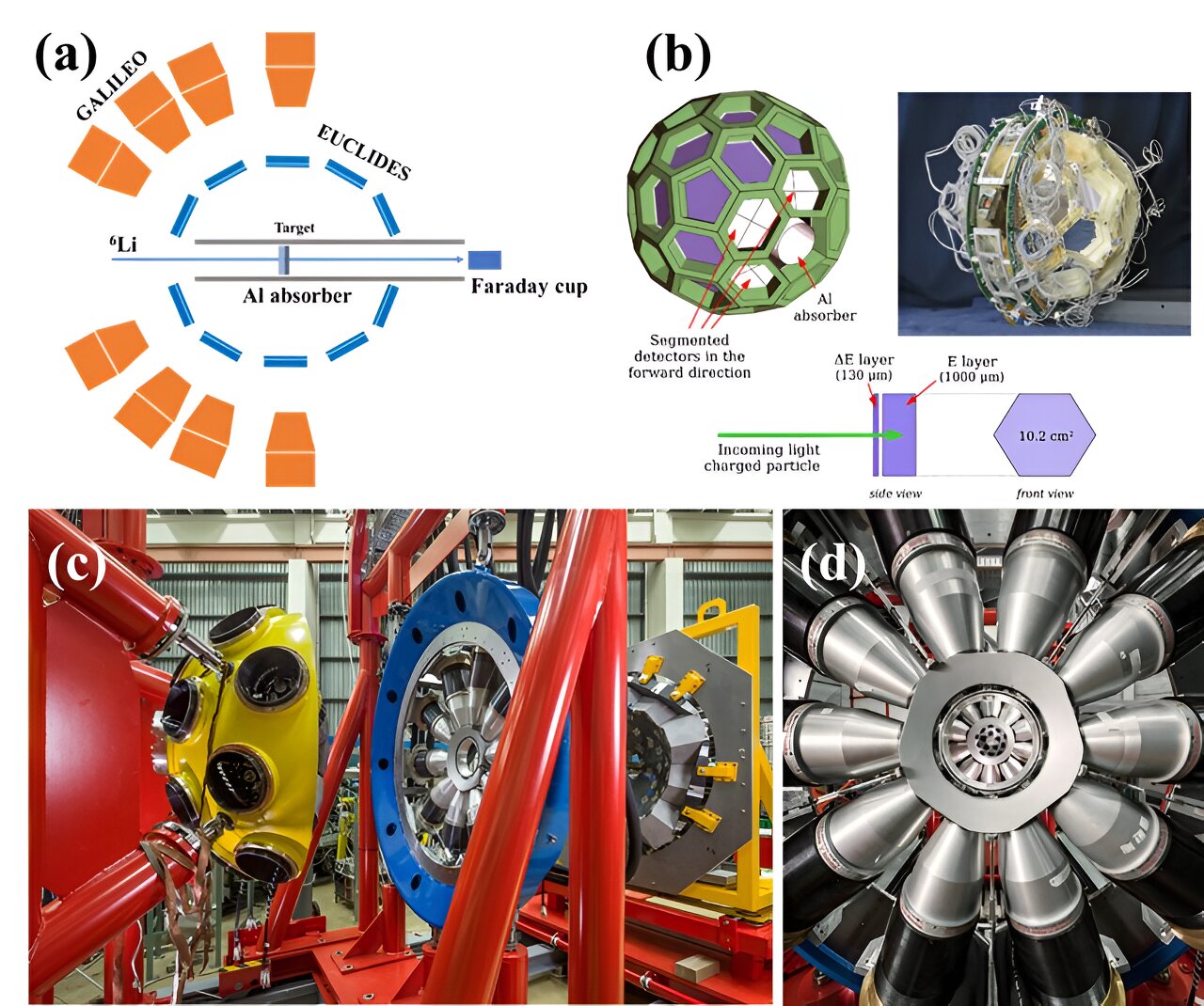
Using the advanced GALILEO Array in combination with the 4π Si-ball EUCLIDES, the researchers performed in-depth spectroscopic analyzes to monitor and identify the reactions. The gamma-gamma coincidence method was crucial in isolating specific reaction channels, allowing the team to determine the behavior of nuclei under different conditions with high accuracy. (https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-024-01462-w). Credit: Zhang, Gaolong
× close to
Using the advanced GALILEO Array in combination with the 4π Si-ball EUCLIDES, the researchers performed in-depth spectroscopic analyzes to monitor and identify the reactions. The gamma-gamma coincidence method was crucial in isolating specific reaction channels, allowing the team to determine the behavior of nuclei under different conditions with high accuracy. (https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-024-01462-w). Credit: Zhang, Gaolong
Researchers have made significant progress in understanding the transfer of neutrons in weakly bound nuclei. The experiment, conducted at the Legnaro National Laboratory, focused on the stripping process of one neutron in reactions involving lithium-6 and bismuth-209. The work has been published in the magazine Nuclear Science and Techniques.
The joint research efforts have shown that the single neutron stripping process produces results comparable to those of full fusion reactions, especially in energy regions near nuclear barriers. Contrary to previous expectations, the results indicate that single-neutron transfer plays a dominant role at lower energies, exceeding the output of fusion reactions.
This research builds on decades of research into the interaction of weakly bonded nuclei such as lithium-6 with heavier nuclei. Lithium-6 is known for its delicate structure, making it prone to breakdown and participating in complex reaction pathways. The study confirmed that even as the energy decreases, the impact of these reactions remains significant, providing new data on how nuclear interactions occur under different conditions.
Using the advanced GALILEO Array in combination with the 4π Si-ball EUCLIDES, the researchers performed in-depth spectroscopic analyzes to monitor and identify the reactions. The gamma-gamma coincidence method was crucial in isolating specific reaction channels, allowing the team to determine the behavior of nuclei under different conditions with high accuracy.
The research group collaborates with international research institutes such as Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen University, Universita di Padova and the Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro. The Advanced Gamma Detection Array and the Charged Particle Detection Array have been carried out to conduct research on nuclear reactions and nuclear structures involving stable, weakly bonded nuclei at large-scale scientific facilities such as the National Laboratory of Legnaro (LNL) in Italy and the China Institute of Atomic Energy , promoting the development of relevant theoretical models as well as the rapid improvement of experimental techniques and measurements. (https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-024-01462-w). Credit: Zhang, Gaolong
× close to
The research group collaborates with international research institutes such as Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen University, Universita di Padova and the Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro. The Advanced Gamma Detection Array and the Charged Particle Detection Array have been carried out to conduct research on nuclear reactions and nuclear structures involving stable, weakly bonded nuclei at large-scale scientific facilities such as the National Laboratory of Legnaro (LNL) in Italy and the China Institute of Atomic Energy , promoting the development of relevant theoretical models as well as the rapid improvement of experimental techniques and measurements. (https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-024-01462-w). Credit: Zhang, Gaolong
Improved nuclear deployment strategies
“By better understanding the behavior of nuclei under these conditions, we can improve our approaches to nuclear energy production and radiation therapy,” said J. Lubian, the study’s corresponding author. This research paves the way for potential applications in medical physics and energy research, where accurate knowledge of nuclear processes is crucial.
The single neutron stripping process underlines the complicated and nuanced nature of nuclear reactions and provides a springboard for future scientific breakthroughs in nuclear science and technology.
More information:
Gao-Long Zhang et al., Stripping process of one neutron in the 209Bi(6Li, 5Li)210Bi* reaction reaction, Nuclear Science and Techniques (2024). DOI: 10.1007/s41365-024-01462-w
Provided by Nuclear Sciences and Engineering